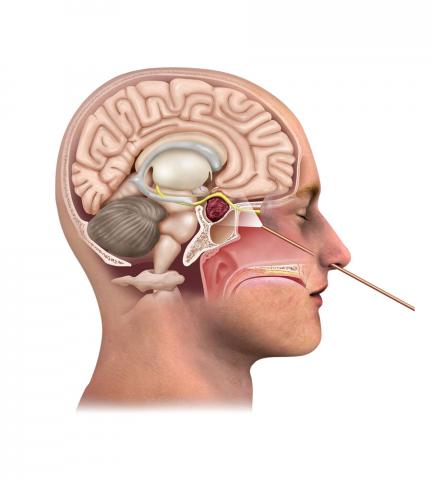
Skull base surgery is a complex and specialized field within neurosurgery that deals with treating various conditions affecting the base of the skull. This intricate region houses critical structures such as the brain, cranial nerves, major blood vessels, and important glands. The surgical procedures performed in this area require meticulous planning, advanced technology, and highly skilled surgeons.
- Anatomy of the Skull Base:
- The skull base forms the floor of the cranial cavity and comprises several bones, including the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and temporal bones.
- It contains important structures such as the pituitary gland, optic nerves, carotid arteries, and cranial nerves.
- Understanding the complex anatomy of the skull base is crucial for successful surgical outcomes.
- Indications for Skull Base Surgery:
- Skull base surgery is indicated for various conditions, including tumors (both benign and malignant), vascular malformations, infections, and traumatic injuries.
- Common tumors treated with skull base surgery include meningiomas, acoustic neuromas, pituitary adenomas, and chordomas.
- Preoperative Evaluation:
- A comprehensive preoperative evaluation is essential to assess the extent of the pathology and plan the surgical approach.
- This evaluation often includes imaging studies such as MRI, CT scans, and angiography to precisely locate the lesion and its relationship to surrounding structures.
- Surgical Approaches:
- Skull base surgery employs various approaches depending on the location and nature of the lesion.
- Traditional open approaches may involve craniotomy or facial incisions, while minimally invasive techniques such as endoscopic surgery are becoming increasingly common.
- The choice of approach aims to minimize morbidity and maximize tumor resection while preserving neurological function.
- Intraoperative Techniques:
- Advanced intraoperative navigation systems, such as stereotactic guidance and neuronavigation, assist surgeons in precisely locating and accessing the target area.
- Intraoperative monitoring of neurological function helps to ensure the safety of critical structures during surgery.
- Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation:
- Postoperative care focuses on pain management, monitoring for complications such as cerebrospinal fluid leaks or infections, and rehabilitation to optimize recovery.
- Patients may require multidisciplinary care involving neurosurgeons, otolaryngologists, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists.
- Outcomes and Prognosis:
- The prognosis following skull base surgery varies depending on factors such as the type and stage of the pathology, the extent of surgical resection, and the patient's overall health.
- Advances in surgical techniques, imaging technology, and perioperative care have led to improved outcomes and quality of life for many patients undergoing skull base surgery.