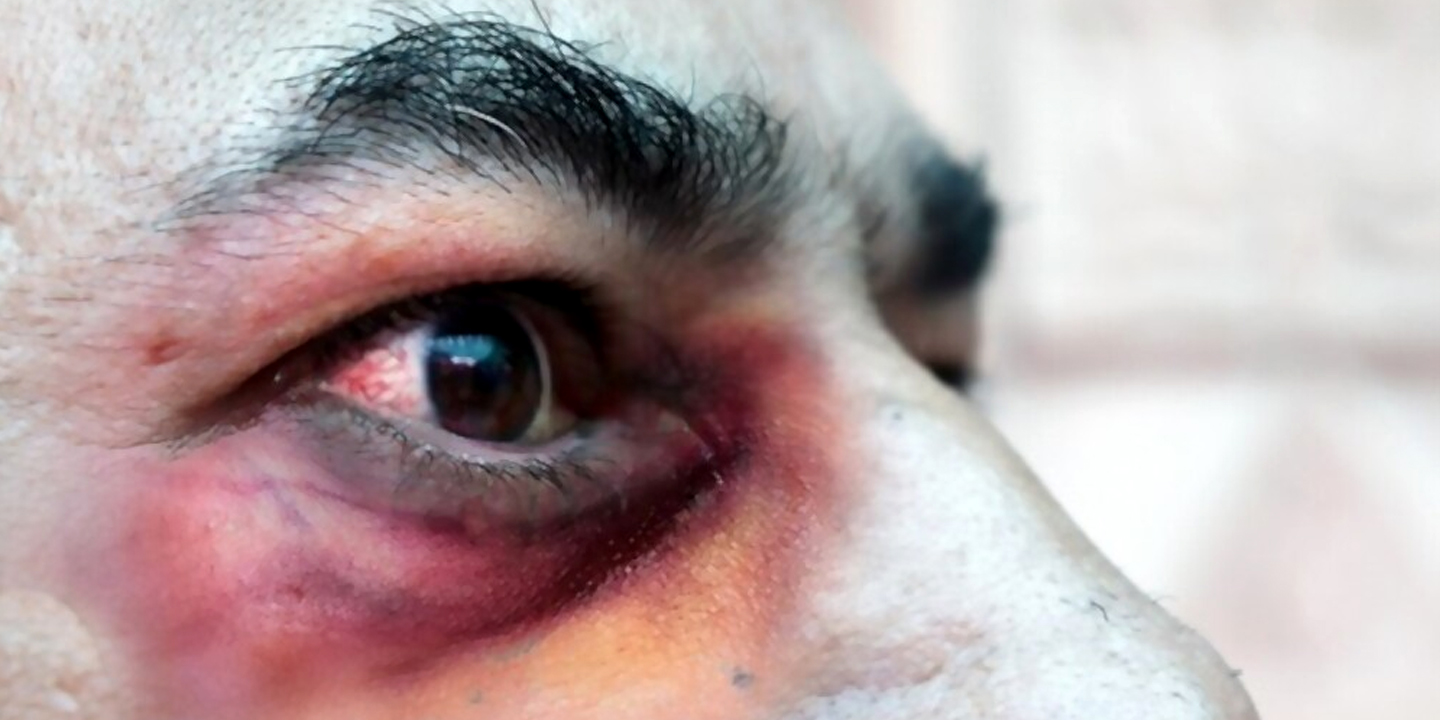
Mucormycosis, commonly referred to as Black Fungus, presents as a rare yet perilous infection. Contact with fungal spores in the environment is the primary cause of Black Fungus. Additionally, it can develop on the skin following penetration by the fungus through cuts, scrapes, burns, or other forms of skin injury.
Fungi naturally inhabit various environments, especially soil and decomposing organic matter like leaves, compost heaps, and decaying wood. This particular fungal infection is attributed to a mold species known as 'mucormycetes'. It's worth noting that individuals with underlying health conditions or those using medications that compromise the body's immune response are particularly susceptible to this uncommon fungal infection.
Mucormycosis, commonly known as black fungus, is caused by a group of fungi called mucormycetes. Several factors contribute to its occurrence:
Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, uncontrolled HIV/AIDS, or certain underlying health conditions, are at a higher risk.
Steroid Usage: Prolonged and inappropriate use of corticosteroids, particularly in the treatment of COVID-19, can elevate the likelihood of black fungus infection.
Poorly Managed Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes, particularly when blood sugar levels are elevated, provides an optimal environment for fungal growth.
Underlying Health Conditions: The risk of contracting mucormycosis is heightened in individuals with conditions such as cancer, organ transplants, or severe burns.
Post-COVID-19: Recovering COVID-19 patients, particularly those treated with steroids, are more susceptible to developing mucormycosis.
Preventive measures, prompt curative treatment and addressing underlying health conditions are important to reduce the risk of black tick infestation.
Black fungus, also known as mucormycosis, may present with a range of symptoms. Typical indications of mucormycosis include:
These symptoms can vary, and not everyone with mucormycosis will have the same ones. Early treatment is crucial, especially when these symptoms are noticed in individuals with underlying health issues like diabetes or recent COPD diagnosis. For mucormycosis, prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital for improving outcomes.
Treating black fungus (mucormycosis) typically involves:
Administering Antifungal Medications: This includes intravenous antifungal drugs like amphotericin B to combat fungal infections.
Performing Surgical Debridement: Surgery is conducted to remove infected and dead tissue, preventing the fungus from spreading further.
Managing Underlying Conditions: Special attention is given to controlling underlying health issues, particularly diabetes, to create an environment less conducive to fungal growth.
Limiting Steroid Usage: Efforts are made to minimize or halt the use of immunosuppressive drugs, especially steroids, which can exacerbate the infection.
Adopting a Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among infectious disease specialists, optometrists, and other healthcare providers ensures comprehensive and coordinated care.
Monitoring Regularly: The patient's condition is continuously monitored, and the treatment plan is adjusted as needed to ensure optimal progress.