Skull sinus surgery, also known as sinus surgery or sinusitis surgery, is a medical procedure
performed to alleviate chronic sinusitis and related conditions. This surgical intervention
aims to improve sinus drainage, reduce inflammation, and enhance overall sinus function.
Here, we delve into the intricacies of skull sinus surgery to provide a comprehensive
understanding of its process, benefits, and considerations.
-
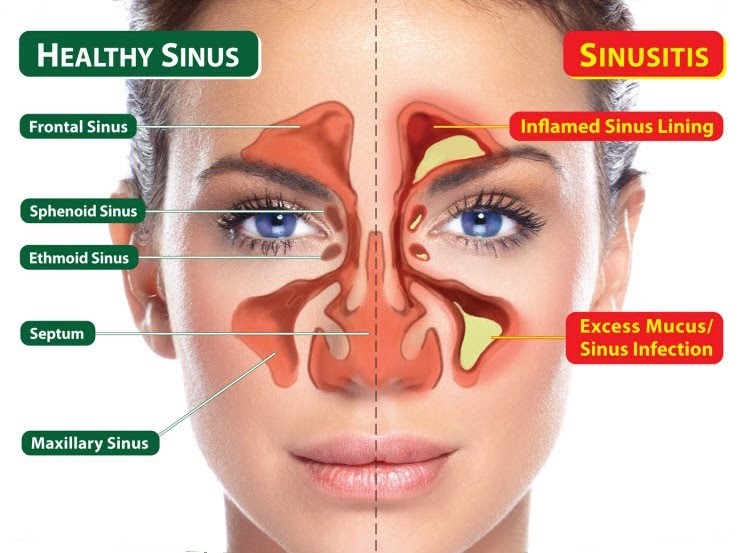
What are Sinuses?
- Sinuses are air-filled cavities located within the bones of the skull.
- They are lined with mucous membranes and connected to the nasal passages.
- Sinuses play a crucial role in filtering, humidifying, and warming inhaled air.
-
Indications for Skull Sinus Surgery:
- Chronic sinusitis that does not respond to conservative treatments like
antibiotics or nasal corticosteroids.
- Recurrent sinus infections.
- Structural abnormalities in the sinuses obstructing proper drainage.
- Nasal polyps causing obstruction and inflammation.
- Tumors affecting the sinuses.
-
Preparing for Surgery:
- Comprehensive evaluation by an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist.
- Imaging studies like CT scans to assess sinus anatomy.
- Discussion of risks, benefits, and alternative treatment options.
- Pre-operative instructions such as discontinuation of certain medications and
fasting guidelines.
-
Surgical Techniques:
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Utilizes a thin, flexible tube with a camera
(endoscope) to access and remove diseased tissue or obstructive structures
within the sinuses.
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): Focuses on restoring normal sinus
drainage and ventilation by removing blockages and widening the natural
openings.
- Image-Guided Surgery: Incorporates advanced imaging technology to navigate
through complex sinus anatomy accurately.
-
Recovery and Post-operative Care:
- Typically performed as an outpatient procedure.
- Mild discomfort, congestion, and nasal drainage are common in the initial days
post-surgery.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing and address any concerns.
- Nasal irrigation and prescribed medications to manage symptoms and prevent
infection.
-
Potential Risks and Complications:
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- Damage to adjacent structures like the eye or brain.
- Recurrence of sinusitis.
- Changes in sense of smell or taste.